Open Science
Introduction
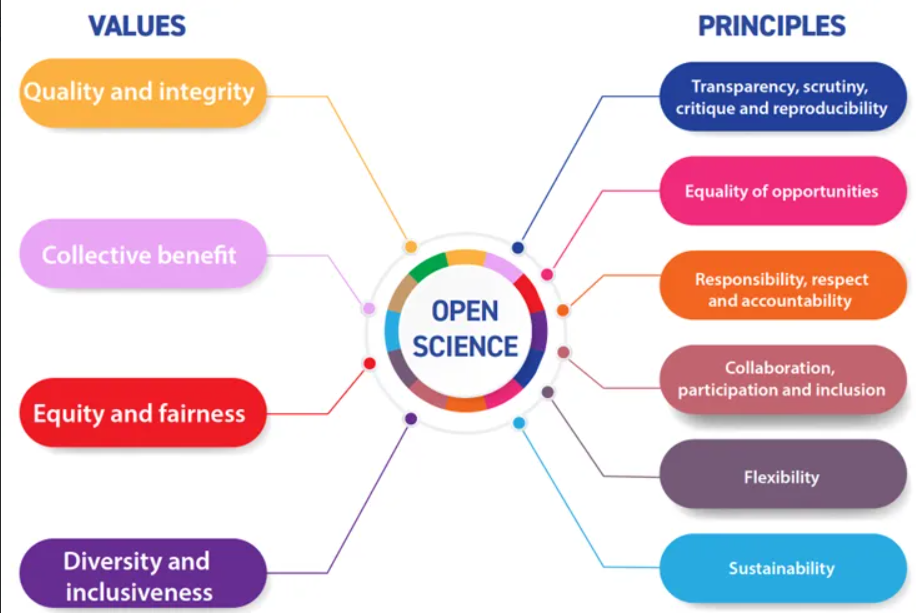
Open Science, also known as “ciência aberta”, refers to the adoption of practices and methods that promote transparency, collaboration and the sharing of processes and results, including data, publications and other elements related to scientific research. This approach allows:
- Open Access to Knowledge: Open science aims to eliminate barriers to accessing scientific knowledge. This is often achieved by making publications, data and other research-related resources freely available.
- Collaboration: Open science encourages collaboration between researchers, institutions and even different sectors of society.
- Reproducibility and Trust: Transparency in research methods and results facilitates reproducibility, a fundamental pillar of scientific validation.
- Innovation and technological advancement: Sharing data, materials and methods can stimulate innovation and technological advancement.
- Public involvement: Making information available to the public in an accessible way can help them to participate in the scientific process, better understand the results and make informed decisions.
- Resource Efficiency: Sharing resources, such as data sets, equipment and infrastructure, can increase efficiency in the use of resources.
- Combating Fraud and Misconduct: Open science contributes to the detection of scientific misconduct, such as fraud and plagiarism. Transparency in research processes makes it easier to identify inappropriate practices and promotes a more ethical culture in the scientific community.
- Rapid Adaptation to Global Challenges: Faced with global challenges such as pandemics, climate change and public health threats, open science allows for a faster and more coordinated response, involving scientists from different parts of the world in the search for solutions.
In short, open science is crucial to promoting a more transparent, collaborative and effective approach, contributing to the advancement of knowledge and responding to complex challenges.
COFAC is aligned with the Open Access Policies of the European Commission and its Open Access requirement in Horizon 2020 and Horizon Europe, and the Policy of the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT). Lusófona University's Self-Archiving Policy for Scientific Production requires publications to be deposited in >RECIL (Lusófona Scientific Repository).
How to Comply with Open Access
Use collaborative online tools to facilitate communication and information sharing with colleagues.
Practicing ethical and transparent conduct at all stages of the process.
Report scientific misconduct when identified.
Participate in science education initiatives.
Share their findings in a way that is accessible to the general public
Participate in online scientific communities where you can share knowledge and discuss discoveries.
Contribute to open source projects, where applicable.
Use open licenses for your work, allowing others to use, modify and share your creations.
Design experiments so that they can be reproduced by other researchers.
Provide software source codes where applicable to facilitate replication.
Collaborate with other researchers, sharing ideas, resources and results.
Consider co-authorship with colleagues who have contributed significantly to the project.
Describe in detail the materials and methods used in your research.
Provide enough information to allow the experiments to be replicated.
Make data available in an open and accessible way.
Use repositories to store and share data.
Publish the results in open access journals.
Open Science Training
Online Training
MOOC “The Essentials of Research Data Management”: the MOOC on research data management is an online course promoted by the General Secretariat for Education and Science with technical development by the Documentation Services of the University of Minho, made available on the NAU Platform at https://lms.nau.edu.pt and which seeks to respond to various existing training needs with regard to research data management. The “Essentials of RDI” course focuses on the main components for a broad and functional understanding of the processes associated with data management throughout the research lifecycle.
FOSTER Open Science Toolkit: online training resource that provides more than ten courses on the practice of open science, developed within the framework of the European Project coordinated by the Documentation Services of the University of Minho “FOSTER Plus - Fostering the practical implementation of Open Science in Horizon 2020 and beyond”.
FOSTER Open Science training handook, is a manual dedicated to providing content and pedagogical tools for training in different Open Science topics. Produced within the framework of the FOSTERplus project, it is a training guide for trainers that has already been translated into Portuguese and is aimed at support staff for research activities as well as researchers.
The Responsible Research and Innovation project (IIR Tools) was funded by the European Commission's 7th Framework Program. It developed a working definition of “responsible research and innovation” and generated a catalog of practices that illustrate what RRI should look like in everyday life. This project identified the actions and support needed, resulting in the production of a vast toolkit, from training to educational resources, to support anyone looking to introduce RRI principles into their research and innovation processes.
Annual National or International Events
Additional information
Guidelines, policies and good practices related to Open Science.
These documents are produced by leading European institutions in the research ecosystem and aim to guide universities, research centers and researchers in adopting practices in line with the principles of Open Science.
Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT):
European Commission - Horizon 2020:
EUA - European University Association:
EUA Roadmap on Open Access to Research Publications Towards Open Access to Research Data EUA Roadmap on Research Assessment in the Transition to Open Science
Practical Guide to the International Alignment of Research Data Management
Open Science Policy Checklist for Research Performin Organisations (RPOs)